How do moments of force affect engineering problems?
In our last article, we looked at how we can apply principles of energy and power to engineering problems. Now we’re going to dive into how moments of force can be applied to engineering problems.
Moments
If we want to describe a force acting on a body, we need to know the magnitude and direction of that force. The effect of the force on a body is that the particle moves in a straight line without turning.
When a force is applied to a rigid body, then the point of application of the force needs to be given, as well as its magnitude and direction. The force can cause the body to experience a rotational motion, with or without a translation of motion. In other words, the body might now turn as well as moving in a straight line.
Imagine we have two forces of unequal magnitude, but want them to produce the same turning effect about a fixed point. To achieve this, the point of application of the smaller force should be at a greater distance from the fixed point than that of the larger force. You can see a diagram showing this below:

The moment of a force, F, about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the diagram at point O is the product of the force and the perpendicular distance x of its line of action from O.
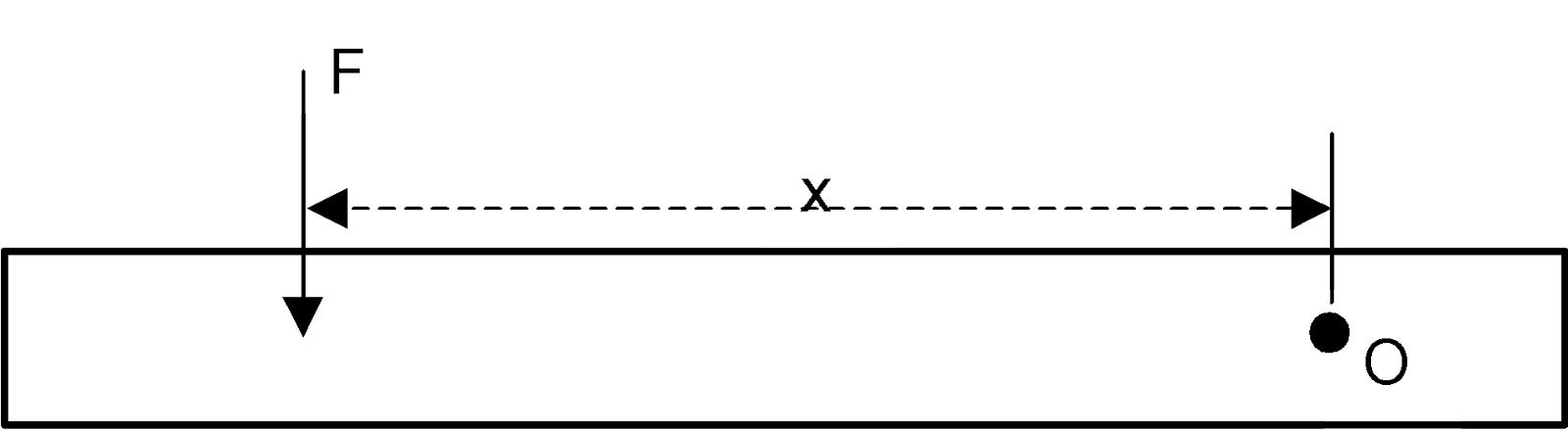
The diagram shows Moment of F about O = Fx anticlockwise. The units of a moment are Nm, and a moment is sometimes called a torque, T.
Couple
The moment produced by two equal and opposite parallel forces that don’t act in the same straight line is called a couple. The moment produced by a couple is equal to the product of one of the forces and perpendicular distance between their lines of action.
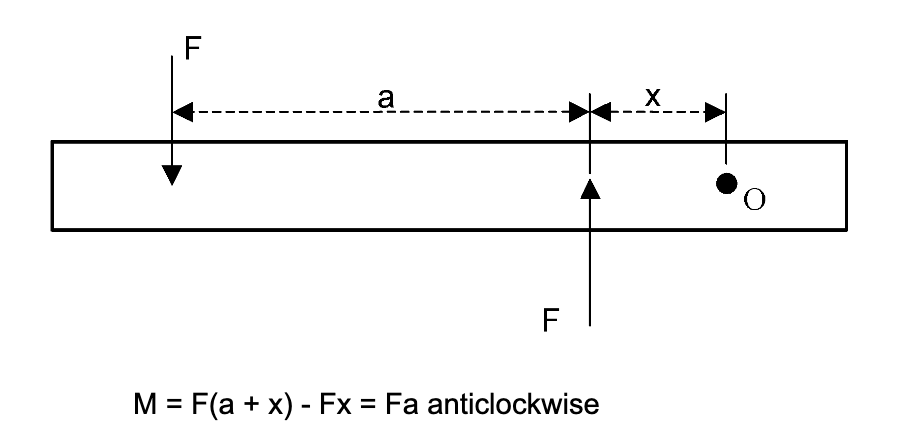
The moment is independent of the distance, X, and is the same about any point in the same plane. In the image below we can see a wrench. The use of the wrench applies a force, F, at a perpendicular distance from the turning point. In this case the turning point is the centre of the nut. The turning moment, or torque, applied is force x perpendicular distance.
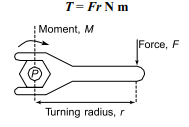
Let’s check out an example to see how this can work. Imagine a pulley wheel with a diameter of 500mm. It has a force of 1000N applied at the rim, and we’re going to work out the torque when this happens.
Torque T = Fr, where force F = 100N and radius r =500/ 2 = 250 mm = 0.25m.
Hence, torque, T = (100)(0.25) = 25 Nm
Sum of Moments
When several forces are lying in the same plane and act on a body, the moments about any point can be added. We need to take into account the sense of rotation for each moment. Imagine that forces of magnitude three end, 4 N and 5 N are applied to a beam of length 6 metres as shown in the diagram:
Moments about point A, clockwise, can be taken as:
- Moment of the 3N force about A is: 3×0 = 0Nm
- Moment of the 4N force about A is: 4×4=16Nm anti-clockwise (ACW) so -16Nm
- Moment of the 5N force about A is: 5×6=30 Nm CW so +30Nm
The Total Moment about point A = -16+30 = +14Nm (CW)
Keep an eye out for our next articles looking into how fluids and heat can affect engineering problems.
Interested in our courses?
You can read more about our selection of accredited online mechanical, electrical, civil and aerospace engineering courses here.
Check out individual courses pages below:
Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Diploma in Electrical Technology
Diploma in Renewable Energy (Electrical)
Higher International Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Diploma in Sustainable Construction
Diploma in Structural Engineering
Diploma in Building and Construction Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Civil Engineering
Higher International Diploma in Civil Engineering
Diploma in Aerospace Structures
Diploma in Principles of Flight
Diploma in Aerodynamics, Propulsion and Space
Higher International Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Mechanical Engineering
Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Diploma in Mechanical Technology
Alternatively, you can view all our online engineering courses here.
Recent Posts
Starting Your Engineering Journey: The Higher International Certificate (Level 4)
Starting Your Engineering Journey: The Higher International Certificate (Level 4) Embarking on a career in engineering is a significant decision, and choosing the right starting point can make all the difference. The Higher International Certificate (HIC) from iLearn Engineering® offers a flexible, accessible, and globally recognised route into the profession. Whether you are beginning your […]
Understanding Qualification Levels and Credits: a guide for engineering students
Understanding Qualification Levels and Credits: a guide for engineering students 1. Introduction to Qualification Levels 2. What Are Credits and Why Do They Matter? While 120 credits is broadly equivalent to one academic year, in traditional university settings this would usually be delivered across approximately 39 weeks with fixed timetables. In contrast, asynchronous learning models—such […]
What is Inertia and how to Calculate it ?
What is Inertia and how to Calculate it ? Inertia is the property of matter that causes it to resist changes in its velocity. This includes changes to the object’s speed or direction of motion. Inertia is directly related to mass, the greater the mass, the greater the inertia. In simple terms: “An object in […]

