How can continuity affect engineering problems?
In our previous article, we looked at how heat and temperature can affect engineering problems. In this article, we’re going to look into continuity and how it affects engineering problems.
What is continuity?
If we consider a steady flow at velocity, v, of a fluid with a density of p. This flow is through a pipe with varying cross-section, A, that you can see in the image below:
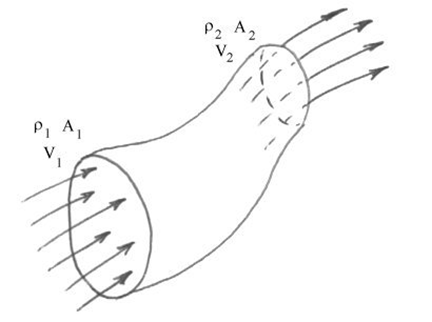
The equation of continuity states that the rate of mass entering the pipe has to be equal to the rate of mass leaving the pipe. This is a state of the principle of conservation of mass.
The mass flow rate,ṁ, is defined as:
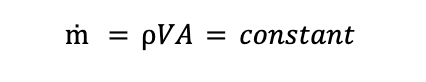
Therefore, if we consider the two stations 1 and 2 that are shown in the image above, we can say that:
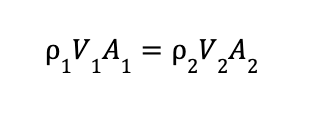
Incompressible Continuity Equation
We can define the Mach number, M, using this equation:
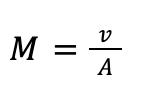
Here, v represents the mean local flow velocity, measured in m/s. Also, a represents the local speed of sound. The speed of a sound is a function of the fluid and temperature. If we have v = a and M = 1, then this represents a flow speed that is equal to the speed of sound.
If we have a relatively low-speed flow, of M as less than 0.3, then it can be assumed to be incompressible. This means that the density can be considered to be constant. Therefore, we can state that a simplified version of the continuity equation for incompressible flow would be:
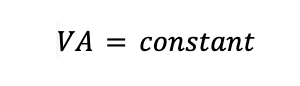
And therefore:
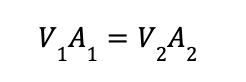
Real-life examples
Let’s have a look at some real life examples to see how this works. If we take the convergent duct that’s in the image below, we can calculate the flow speed at the exit, which is point 2.
Our continuity expression, as we’ve seen above, is:
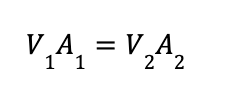
Now, if we rearrange if with respect to the unknown parameter, we will get:
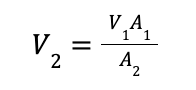
Now, we can substitute the values we have, and solve the equation:
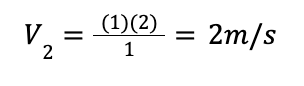
We can do a sanity check on our equation to make sure it’s right. The area of the duct has reduced going from station 1 to station 2, or from the entrance to exit. Going by continuity, and to be able to maintain the constant value of mass flow there has to be a corresponding increase in velocity. The flow speed has increased, and we can see this from our solution. This gives us an additional sanity check to ensure our answer is correct.
We can use the same equation to solve an incompressible fluid flowing through a pipe with a diameter of 20mm. The velocity of the fluid is 10m/s. If the pipe changes diameter to 25mm, we can calculate the velocity at the point that it changes. Our answer would be 6.4m/s, and we can use a similar sanity check to ensure our answer is correct.
Keep an eye out for our next article looking into how ideal gas laws can affect engineering problems.
Interested in our courses?
You can read more about our selection of accredited online mechanical, electrical, civil and aerospace engineering courses here.
Check out individual courses pages below:
Diploma in Aerospace Structures
Diploma in Principles of Flight
Diploma in Aerodynamics, Propulsion and Space
Higher International Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Mechanical Engineering
Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Diploma in Mechanical Technology
Alternatively, you can view all our online engineering courses here.
Recent Posts
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained Introduction In this blog we will identify the main components within an aircraft, more from the point of view of large external parts, more specifically, flight control surfaces. Flight control surfaces are simply physical devices that the pilot can control and adjust in order to change […]
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters Introduction The performance of a generator is often judged by how efficiently it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Understanding and calculating this efficiency, along with other key output parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and load, is essential for evaluating performance and ensuring reliable operation. […]
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter Introduction Generators produce a significant amount of heat and electrical stress during operation, which can affect performance and lifespan if not properly managed. That’s where cooling and protection devices come in. These essential systems, including fans, radiators, circuit breakers, and relays, work together […]

