What are the principles of operation of a DC electric motor?
In our last article, we looked at the electrical parameters in series and parallel electrical circuits. In this article, we’re going to dive into the principles of operation of a DC electric motor.
The motor effect
When a current-carrying conductor is placed on a magnetic field, the conductor will experience a force. This is called the motor effect
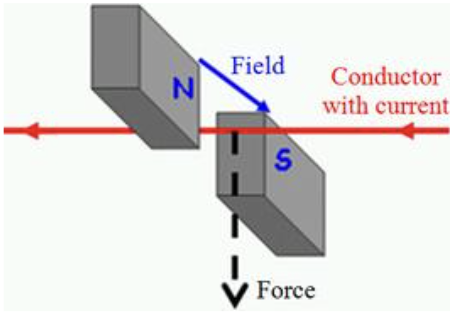
It’s down to interaction between magnetic fields.

A magnetic field from a magnet interacts with the magnetic field due to current in the wire. A combined magnetic field is produced which is stronger at region A and weaker at region B. A force then acts on the wire from the stronger field to the weaker field.
Fleming’s left-hand rule
The simplest way to determine the direction of force is to use Fleming’s left-hand rule:
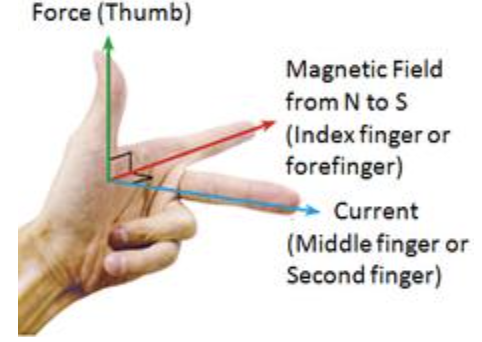
The rule states that the direction of force (indicated by the thumb) is perpendicular to both the direction of magnetic field from the North to South pole (indicated by the index finger) and the direction of current (indicated by the middle finger).
From this rule, we can see that the direction of force depends on the direction of the magnetic field, and the direction of current. If the direction of current is parallel to the direction of the magnetic field, there will be no force produced. The magnitude of force is maximum when the direction of current is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field.
D.C Motor
A d.c motor makes use of the turning effect of a current carrying-coil in a magnetic field to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
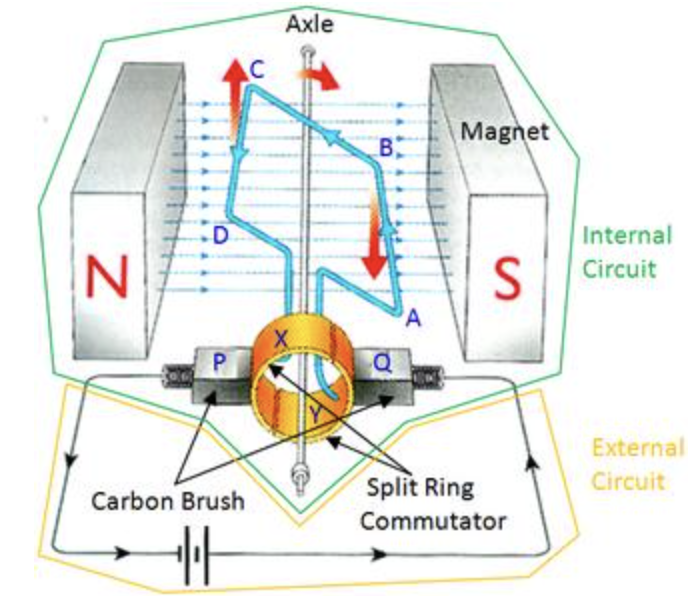
How does it work? Current flows from Q to Y, goes through the coil ABCD and out through X to P:
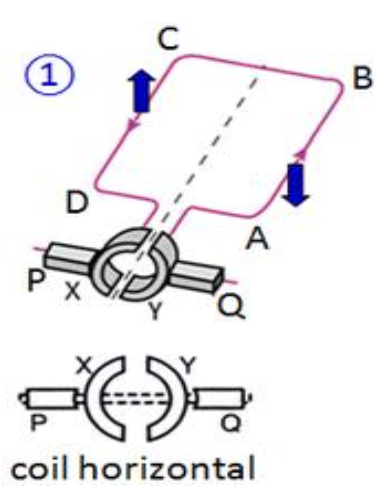
Using Fleming’s left-hand rule, a downward force acts on AB, and an upward force on CD. the coil will then rotate clockwise about an axle until it reaches the vertical position:
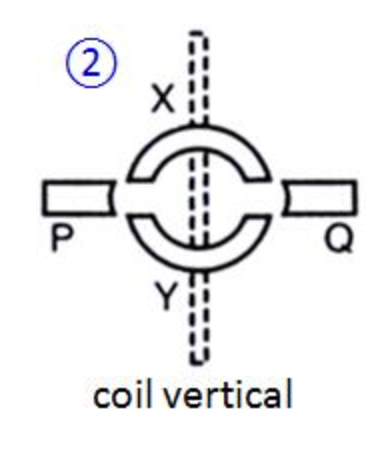
When the coil is at the vertical position, no current flows as neither X or Y is in contact with P or Q:
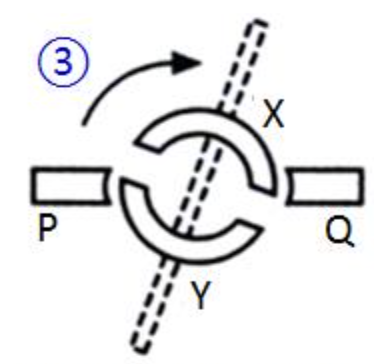
The momentum of the coil, however, carries it past the vertical position. The half ring Y now touches P and X touches Q. Current flows from Q to X, goes through the coil DCBA and out through Y to P. The current is reversed in the coil:
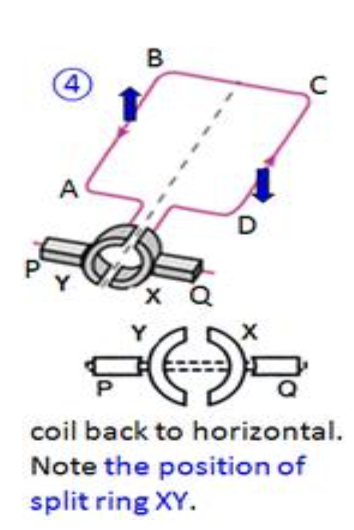
Using Fleming’s left-hand rule, a downward force acts on CD and an upward force on AB. The coil continues to rotate in a clockwise direction.
Factors affecting the d.c motor
The turning effect of a coil can be increased by
- Increasing the current in the coil.
- Increasing the number of turns on the coil per unit length.
- Using a stronger magnet.
- Inserting a soft iron core into the coil.
Take the diagram below. It shows a simple d.c motor with a coil ABCD rotating between the poles of a strong permanent magnet:
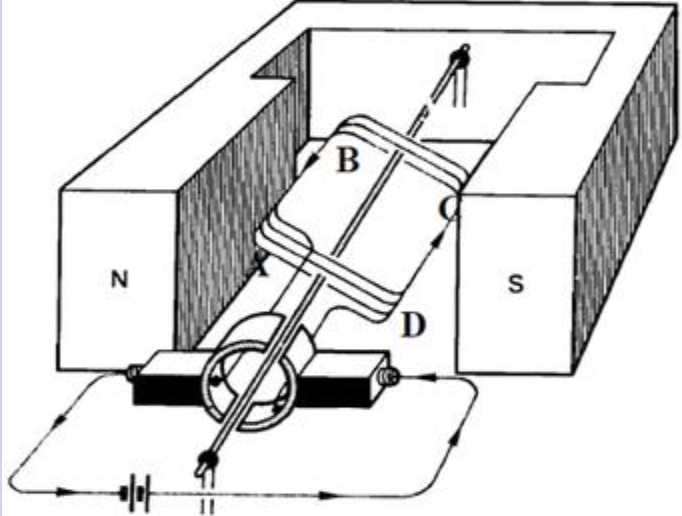
We can see that the direction of forces is that AB is upwards and CD is downwards. The direction of the moment produced is clockwise.
The presence of the split ring commutator reverses the current in the coil every half a revolution, which reverses the direction of force acting on AB and CD. This ensures the coil to rotate in the same direction.
Note that the forces acting on AB or CD are always upwards or downwards.
Remember: moment = force x perpendicular distance from pivot
So when the coil is vertical it will have 0 perpendicular distance, so the graph is at 0
Since the coil always rotates in the same direction, the waveform is also in the same direction.
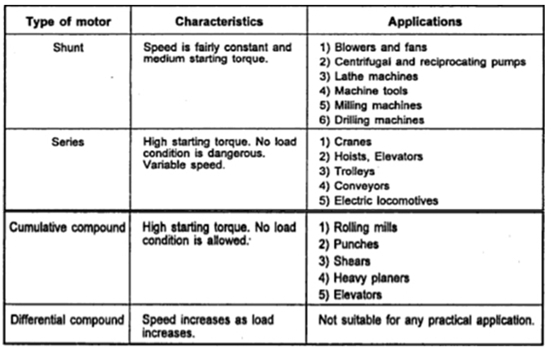
Applications of d.c motors
There are 4 main types of d.c motors, the table below shows the application of each type, depending on their characteristics:
Keep an eye out for our next articles looking into Kirchhoff’s current and voltage laws.
Interested in our Electrical Engineering Courses?
At iLearn Engineering®, we offer a diverse range of online accredited electrical engineering courses and qualifications to cater to different academic and career goals. Our courses are available in varying credit values and levels, ranging from 40 credit Engineering Diplomas to a 360 credit International Graduate Diploma.
Short Courses (40 Credits)
A selection of our more popular 40 credit electrical diplomas…
Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Diploma in Electrical Technology
Diploma in Renewable Energy (Electrical)
First Year of Undergraduate (Level 4 – 120 Credits)
Higher International Certificate in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
First Two Years of Undergraduate (Level 5 – 240 Credits)
Higher International Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering.
Degree equivalent Graduate Diploma (Level 6 – 360 Credits)
International Graduate Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
All Electrical and Electronic Courses
You can read more about our selection of accredited online Electrical and Electronic Engineering courses here.
Complete Engineering Course Catalogue (all courses)
Alternatively, you can view all our online engineering courses here.
Recent Posts
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained
Aircraft Basics: Main Components and Standard Control Surfaces Explained Introduction In this blog we will identify the main components within an aircraft, more from the point of view of large external parts, more specifically, flight control surfaces. Flight control surfaces are simply physical devices that the pilot can control and adjust in order to change […]
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters
Understanding and Calculating Generator Efficiency and Output Parameters Introduction The performance of a generator is often judged by how efficiently it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Understanding and calculating this efficiency, along with other key output parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and load, is essential for evaluating performance and ensuring reliable operation. […]
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter
Essential Cooling and Protection Devices: How They Work and Why They Matter Introduction Generators produce a significant amount of heat and electrical stress during operation, which can affect performance and lifespan if not properly managed. That’s where cooling and protection devices come in. These essential systems, including fans, radiators, circuit breakers, and relays, work together […]

