Introduction to the Capacitor in Electrical Engineering
We can think of capacitors are short term ‘charge-stores’. In other words, capacitors just store charge inside them. A capacitor consists of two metal plates separated by a layer of insulating material called a dielectric.
There are 2 types of capacitor:
- Electrolytic capacitors. These hold much more charge and must be connected with the correct polarity, otherwise they can explode.
- Non-electrolytic. These hold less charge and can be connected either way round in a circuit.

How Does a Capacitor Work?
When two conducting plates are connected to a battery, electrons move towards one plate. The positive plate loses electrons , eventually leaving both plates with equal and opposite charge, +Q and -Q. When a capacitor is charged, we say that the capacitor has charge Q.

Define Capacitance
Capacitance, C = “the charge, Q, required to cause potential difference, V, in a conductor. It is measured in Farads”.
“1 Farad is the capacitance of a conductor, which has potential difference of 1 volt when it carries a charge of 1 coulomb”.

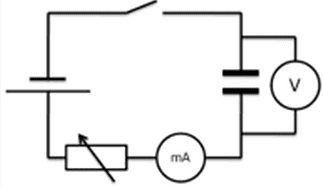
Charging a Capacitor Using D.C.
At any time, t, after the switch is closed, the charge, Q, on the capacitor can be calculated using Q=It where I = the current (Amps).
The variable resistor can be altered to keep the current constant.
Plot a graph of capacitance against voltage and since:
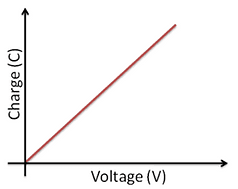
The gradient of the graph will equal the capacitance of that capacitor.
Charge Stored in a Capacitor
Electrical potential energy is stored when a capacitor is charged.
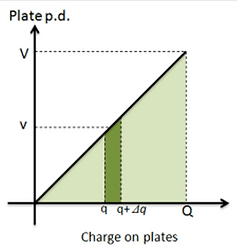
The area under this graph is equal to the energy stored = (½bh)
We can combine previous equations to give the following:
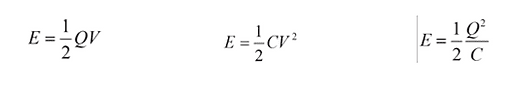
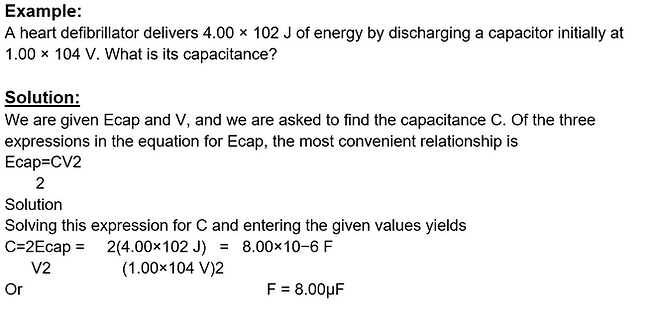
Charging and Discharging a Capacitor
When discharging, the current decreases with the potential difference, p.d. This decrease is exponential as can be seen below. Q0, V0 and I0 are all the initial charge, voltage and current through the capacitor at the initial discharge.
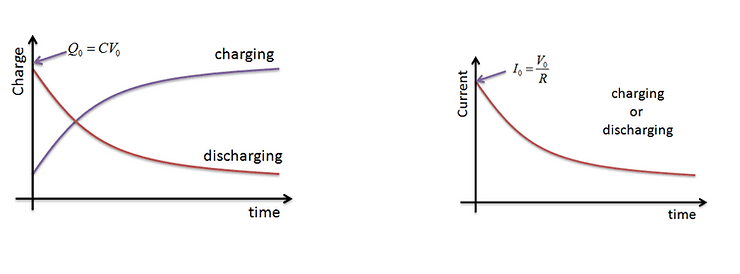
Decay Curve
Let us now examine the process of discharging the capacitor. Charge, Q, falls to 1/e of its initial value in a time equal to the time constant, RC.

When the initial charge is Q0,
- After RC seconds = 0.37 x Q0
- After 2RC seconds = 0.37 x 2 x Q0
- After nRC seconds = 0.37n x Q0.
The time taken to halve, T½, is always the same:
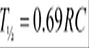
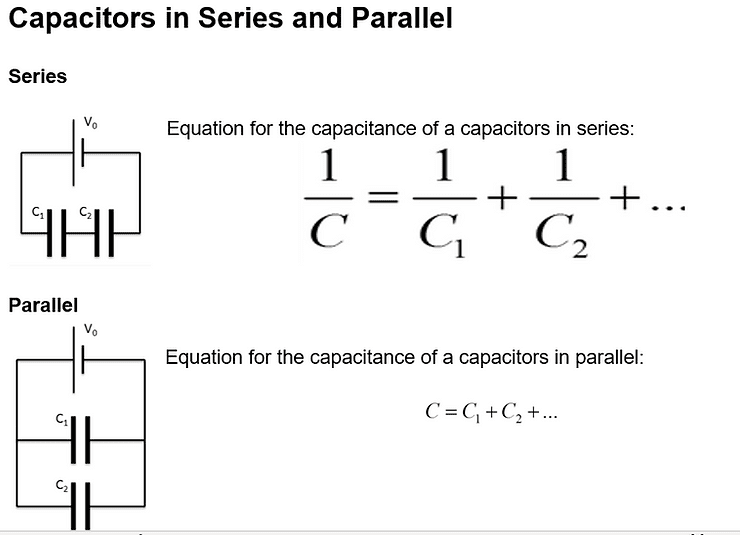
Example of Capacitors in Series and Parallel

Interested in electrical and electronic engineering? Find out more about all the electrical engineering courses we have available by clicking here.
Diploma in Electrical Technology
Diploma in Renewable Energy (Electrical)
Diploma in Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Alternatively, you can view all our online engineering courses here.
Recent Posts
Essential Formulas for Calculating Drilling Parameters
Essential Formulas for Calculating Drilling Parameters When it comes to precision and efficiency in manufacturing, few processes are as foundational—or as critical—as drilling. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or a student entering the world of mechanical or industrial engineering, understanding how to correctly calculate drilling parameters can significantly impact the quality of your work, the […]
From Raw Material to Refined Component: The Role of Drilling and Turning
From Raw Material to Refined Component: The Role of Drilling and Turning Secondary processes are used in manufacturing to further modify the output of primary manufacturing processes in order to improve the material properties, surface quality, surface integrity, appearance and dimensional tolerance. In this blog, we will focus on drilling and turning as secondary manufacturing […]
Behind the Cutter: How Milling Shapes the Future of Manufacturing
Behind the Cutter: How Milling Shapes the Future of Manufacturing Secondary processes are used in manufacturing to further modify the output of primary manufacturing processes in order to improve the material properties, surface quality, surface integrity, appearance and dimensional tolerance. In this blog, we will focus on milling as a secondary manufacturing process. Machining refers […]

