How can we calculate the axial load-carrying capacity of a reinforced concrete column and classify it?
Following on from our previous article on the axial load-carrying capacity of a steel column, we’re going to look at the axial load-carrying capacity of a concrete column and also see how we can classify it.
What is a concrete column?
Reinforced concrete columns are large, normally rectangular, or circular in shape, and not susceptible to buckling. Due to production technology, the possibility of imperfections in reinforced concrete columns is greater than in steel columns. This means the most common failure is due to a combination of axial force and bending moment due to the action of transverse forces.
The design of reinforced concrete columns differs depending on whether it is a short or slender (long) column. So, to design a reinforced concrete column, it is first necessary to determine its slenderness.
What is column slenderness?
Column slenderness is defined as:
λ=Leimin
Where are:
- Le is the effective length of the column.
- imin: minimum radius of gyration; imin=IA,
- I: moment of inertia,
- A is the cross-section area.
The effective length of the column is calculated according to the following expression:
Le=K x L
Where are:
- K is the effective length coefficient, depending on the support conditions,
- L is the length of the column.
Where ψA and ψB are defined as follows:
A=EIa2l1+EIabl2EIa4L1+EIa5L2
B=EIb9l3+EIabl2EIb6L1+EIb7L2
Ψ=0: infinitely rigid connection. In reality, ψ=0.1 for rigid connections. Ψ = ∞ for hinged connections.
Frame supports are considered immovable if their flexibility is low, which applies to:
- horizontally supported supports,
- horizontally unsupported supports, where the influence of node displacement is negligible (the difference between the shear forces according to the 1st and 2nd order theories is less than 10%).
Proof of load-bearing capacity
Proof of load-bearing capacity in a deformed configuration (according to the theory of the 2nd order) does not have to be carried out if the additional bending moments from the axial force are negligible. This is met if one of the conditions below is met:
crit≤25
crit16Ed
Where are:
Ed=NEdAc·fcd
For columns of immovable systems that are not loaded with shear loads between the nodes, it is valid:
crit≤25·2-e01e02 , for e01e02.
Let’s look at an example. Take a 2m-long column with one end that has ψ1 = 1.0 and the other ψ2 = 0.1. It has a cross-section dimension of 40/40cm. The system is immovable, and we’re going to calculate the column slenderness λ.
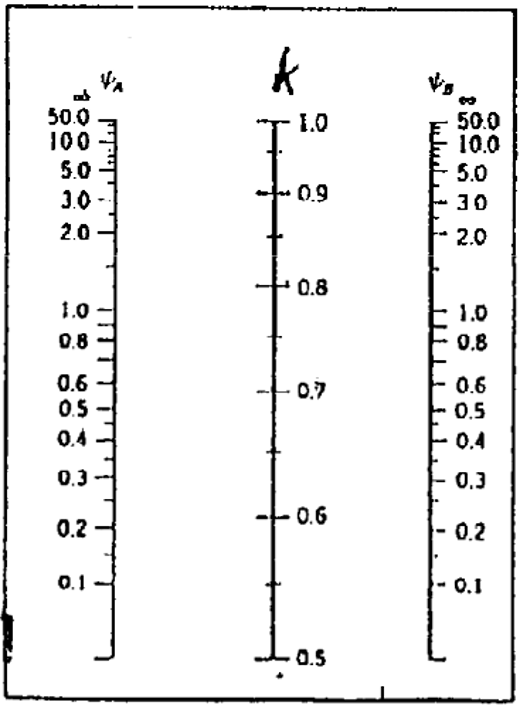
K = 0.65
Le=K x L = 0.65 x 2.0 m = 1.3 m.
A = 0.4 x 0.4 = 0.16 m2
I=b x h312 = 0.4 x 0.4312 = 0.002133 m4
imin=IA=0.0021330.16=0.1155 m
λ=Leimin=1.3m0.1155m=11.25
In our next articles, we’re going to dive into the vibration of various structures and how they are affected, so make sure you check them out.
Interested in our courses?
Interested in civil or mechanical engineering? Find out more about all the civil engineering courses we have available by clicking here, and the mechanical engineering courses by clicking here.
Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Diploma in Mechanical Technology
Diploma in Sustainable Construction
Diploma in Structural Engineering
Diploma in Building and Construction Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Civil Engineering
Higher International Diploma in Civil Engineering
Higher International Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
Higher International Certificate in Mechanical Engineering
Alternatively, you can view all our online engineering courses here.
Recent Posts
Starting Your Engineering Journey: The Higher International Certificate (Level 4)
Starting Your Engineering Journey: The Higher International Certificate (Level 4) Embarking on a career in engineering is a significant decision, and choosing the right starting point can make all the difference. The Higher International Certificate (HIC) from iLearn Engineering® offers a flexible, accessible, and globally recognised route into the profession. Whether you are beginning your […]
Understanding Qualification Levels and Credits: a guide for engineering students
Understanding Qualification Levels and Credits: a guide for engineering students 1. Introduction to Qualification Levels 2. What Are Credits and Why Do They Matter? While 120 credits is broadly equivalent to one academic year, in traditional university settings this would usually be delivered across approximately 39 weeks with fixed timetables. In contrast, asynchronous learning models—such […]
What is Inertia and how to Calculate it ?
What is Inertia and how to Calculate it ? Inertia is the property of matter that causes it to resist changes in its velocity. This includes changes to the object’s speed or direction of motion. Inertia is directly related to mass, the greater the mass, the greater the inertia. In simple terms: “An object in […]

